What is an interest rate floor?
Extra income when rates fall
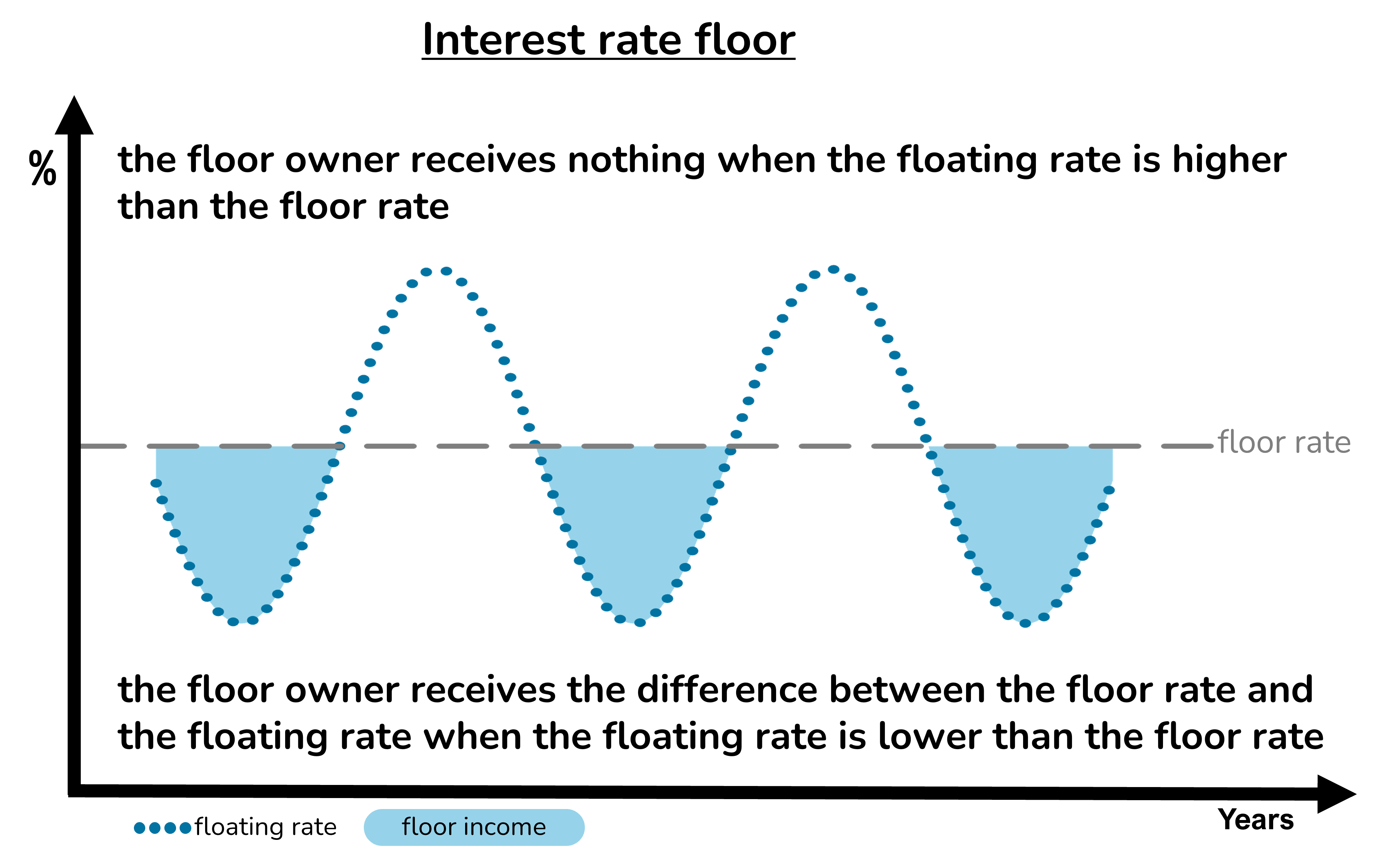
An interest rate floor acts like insurance against low interest rates.
The floor buyer pays a premium for the floor in exchange for extra income when interest rates rise fall below a chosen minimum, the floor rate. The further that rates fall below the floor rate, the greater the extra income from the floor.
The risk of a floor is that the buyer pays a premium for the floor but receives nothing in return, for example if interest rates remain above the floor rate for the duration of the instrument.
Borrowers may buy floors to offset the adverse risks of fixed rate loans.
Applications of floors
To offset adverse floors

Borrowers become exposed to the risks of adverse floors when they they take out collared loans and fixed rate loans.
In each case the borrower effectively pays for an interest rate cap by simultaneously selling an interest rate floor. The cap protects the borrower if interest rates rise. But the adverse floor exposes the borrower to risks if interest rates fall.
The borrower may offset the adverse floor by buying a favourable floor. The strategy effectively transforms collared loans or fixed rate loans into capped loans.
With a capped loan, the borrower pays the floating rate or the cap rate, whichever is the cheaper on each applicable interest payment date.
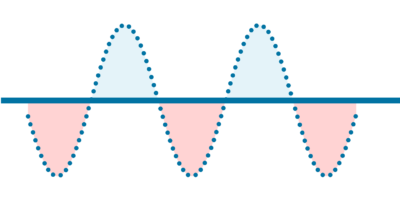
Fixed rate loans
A fixed rate loan is equivalent to a floating rate loan with a cap in favour of the borrower and a floor in favour of the lender.
When the floating rate is higher than the fixed rate, the fixed rate borrower makes an interest saving as the result of the embedded interest rate cap. The further the floating rate exceeds the fixed rate, the greater the interest saving made by the borrower.
When the floating rate is lower than the fixed rate, the fixed rate borrower incurs interest losses as the result of the embedded interest rate floor. The further the floating rate falls below the fixed rate, the greater the interest losses incurred by the borrower.
By buying a favourable floor to offset the adverse floor embedded in the fixed rate loan, the borrower effectively transforms the fixed rate loan into a capped loan.
With a capped loan, the borrower pays the floating rate or the cap rate, whichever is the cheaper on each applicable interest payment date.
Collared loans
A collared loan is a floating rate loan with an embedded interest rate collar.
When the floating rate is between the cap and floor rates of the collar, the borrower pays the floating rate.
When the floating rate is above the cap rate, the borrower pays the cap rate, making an interest saving compared to the floating rate as the result of the embedded cap.
When the floating rate is below the floor rate, the borrower pays the floor rate, incurring an interest loss compared to the floating rate as the result of the embedded floor.
By buying a favourable floor to offset the adverse floor embedded in the collared loan, the borrower effectively transforms the collared loan into a capped loan.
With a capped loan, the borrower pays the floating rate or the cap rate, whichever is the cheaper on each applicable interest payment date.
How is the floor premium paid?
Upfront or in instalments


The premium for a favourable floor is normally paid upfront by the borrower. This is generally the case when the floor is purchased independently of the loan or loans it is hedging.
Some lenders offer deferred premium floors, where the premium is payable in instalments over the life of the floor regardless of what happens to interest rates. By deferring the premium payable, the lender is effectively lending the floor buyer the money to pay the floor premium so will apply a funding charge and may require additional security.
Borrowers may create their own ‘do-it-yourself’ deferred premium payments by borrowing extra to pay the upfront floor premium cost and then repaying the extra amount borrowed in instalments over the life of the floor.
How are floors priced?
Factors influencing the floor premium


For a given interest rate environment, the amount of the floor premium is driven by three factors: the loan amount protected, the duration of the protection and the floor rate.
Amount protected: the larger the amount being protected, the larger the potential pay-out on the floor. Consequently, the floor premium tends to change in proportion with the amount of loan it is hedging.
Duration: the longer its duration, the more likely that the floor will pay out and the more expensive the floor.
Floor rate: the higher the floor rate, the greater the probability that the floor will pay out (and the larger each payment will be). Accordingly, floors with higher floor rates are more expensive than floors with lower floor rates.
For a given floor structure (amount protected, duration and floor rate) the cost of the floor premium will fluctuate over time based on changes in market expectations regarding the future path of interest rates and interest rate volatility.
What are the risks of interest rate floors?
Loss of premium


The worst that can happen is the borrower pays the premium for the floor but does not receive any payments from it, for example if the floating interest rate stays above the floor rate for the life of the instrument.
Provided that the floor premium has been paid, there can never be a penalty to exit a floor early. The floor’s early redemption value will always be positive or zero. The early redemption value of a floor tends to decline as time passes.