About Cap-It
Cap-It was established to improve the availability of interest rate cap protection to small and medium-sized borrowers in the UK.
The public material on this website contains information about the mechanics and risks of current financing alternatives:
- The options page gives a guide to financing options for UK borrowers.
- The strategies page describes how the options may be applied to reduce costs and risks.
- The insights page includes articles about finance and risk management.
- The Glossary contains a list of terms and definitions, with further explanations in the FAQs.
Additional material in respect of potential investments may only be viewed by those persons eligible to view such material. For further information, please view the eligibility section.
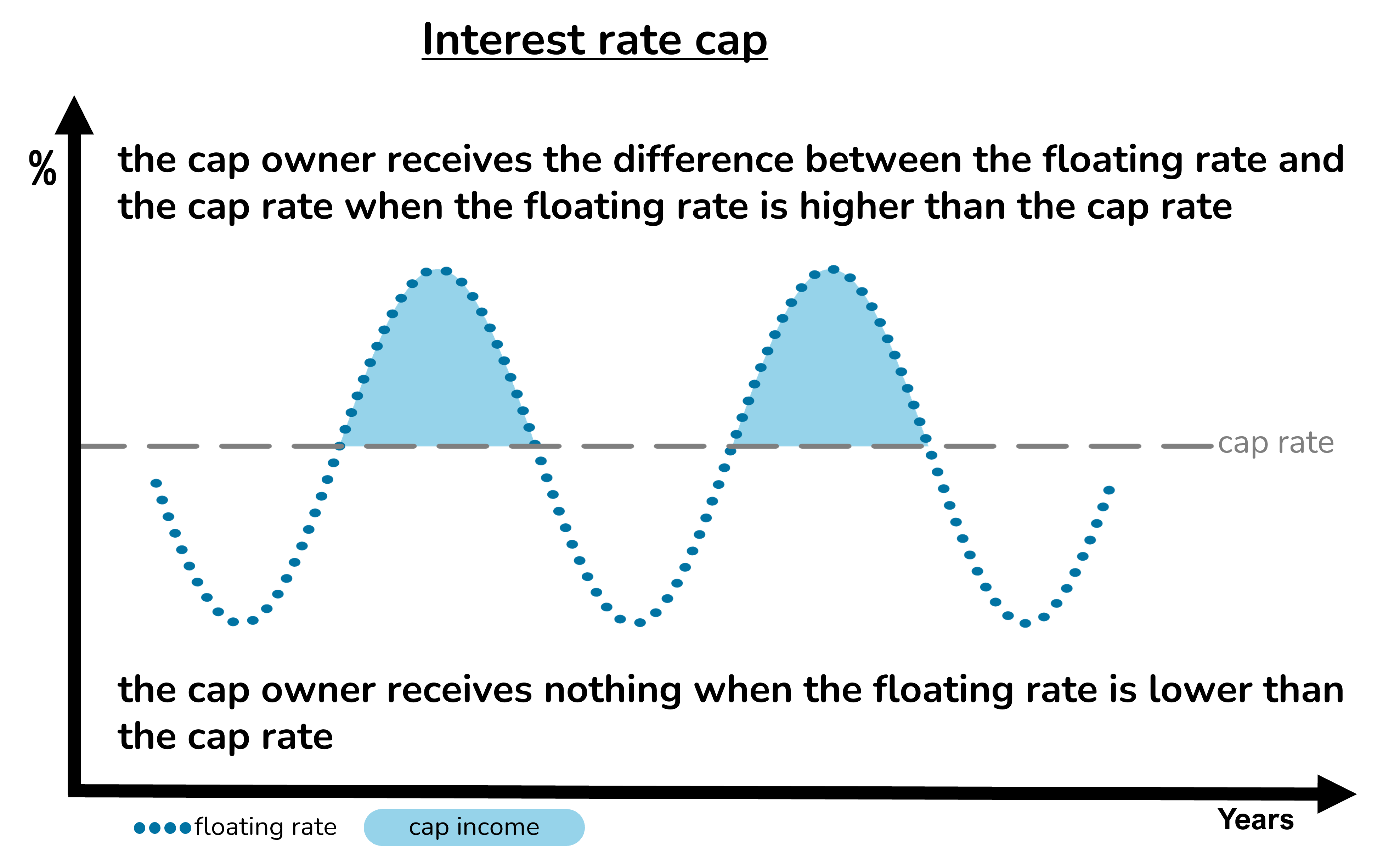
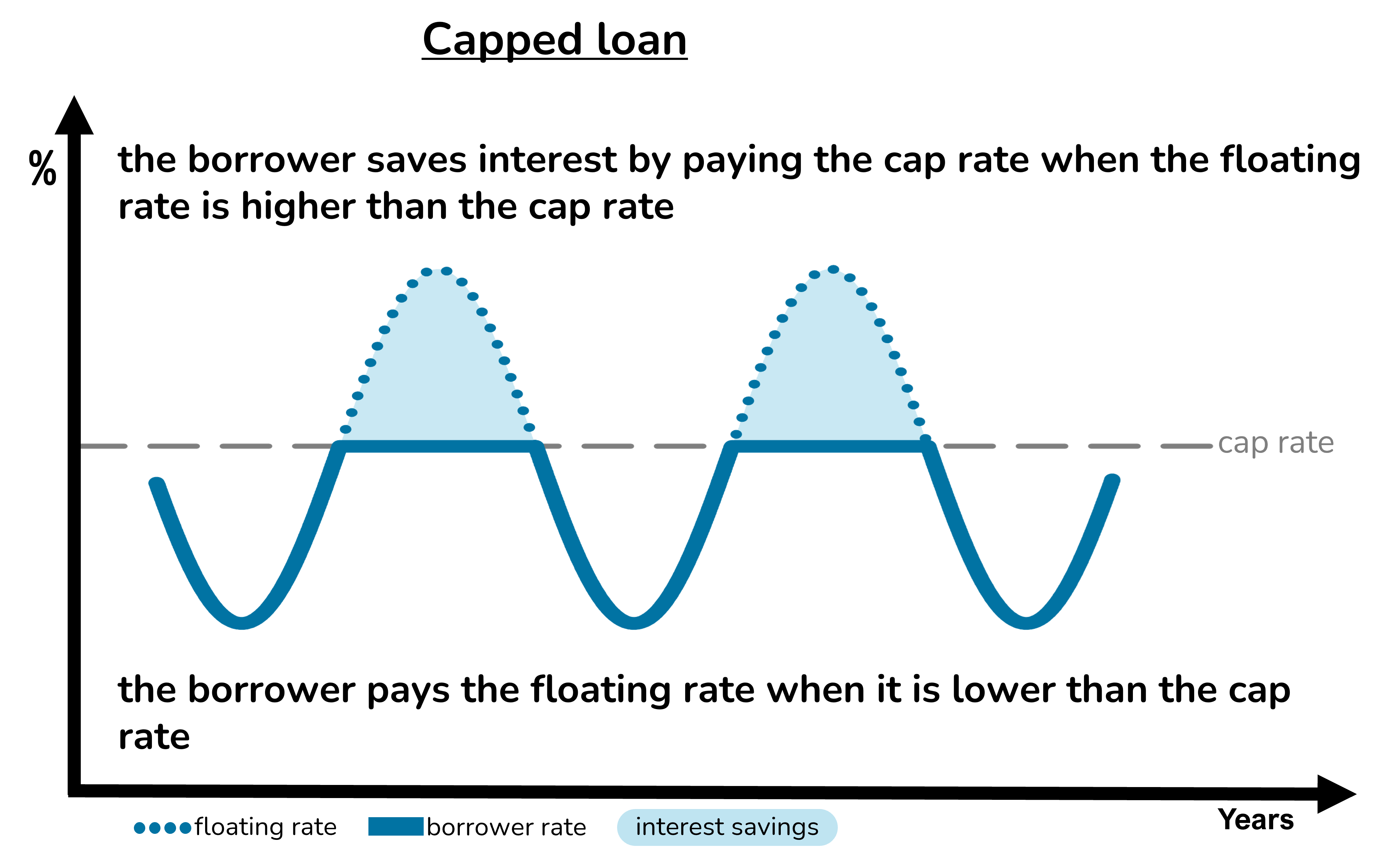
Capped loans
With a capped loan, the borrower pays the floating rate or the cap rate, whichever is the cheaper on each applicable interest payment date:
- When the floating rate is lower than the cap rate, the borrower pays the floating rate.
- When the floating rate is higher than the cap rate, the borrower pays the cap rate.
Capped loans and mortgages are created by combining a normal floating rate or fixed rate loan with a cap or a floor. More here